► Affricate
A sound produced by stopping the air flow then releasing it with friction e.g. / tâ / , / dΩ /.
► Alveolar (ridge)
The ridge at the top of the mouth between the teeth and the hard palate. Several sounds e.g. / t / , / d / are made in this area.
►Consonant
A sound in which the air is partly blocked by the lips, tongue, teeth etc. Any letter of the English alphabet which represents these sounds, e.g. d/d/, c/k/. See diphthong and vowel.
► Consonant cluster
Two or more consonants occurring together at the beginning or end of a syllable e.g. / eks / in / eksáésaˆz / (exercise); / str / in / strÅ ̃ / (strong).
►Contraction
A shorter form of a group of words, which usually occurs in auxiliary verbs, e.g. you have = you’ve; it is = it’s.
►Contrastive stress: see stress.DiphthongA vowel combination which is pronounced by moving from one vowel to another, e.g. / aˆ / as in my is pronounced by moving from / æ /to / ˆ /. See consonant and vowel.
►Diphthong
A vowel combination which is pronounced by moving from one vowel to another, e.g. / aˆ / as in my is pronounced by moving from / æ /to / ˆ /. See consonant and vowel.
►Minimal pair
Two words which differ from each other by only one meaningful sound (or phoneme),e.g. hit / hˆt / ; heat / hˆÄt /.
►Phoneme
The smallest sound unit which can make a difference to meaning e.g. /p/ in pan, /b/ in ban. Phonemes have their own symbols (phonemic symbols), each of which represents one sound. Words can be presented in phonemic script (usually International Phonetic Alphabet or IPA), e.g. / dÅktW /– doctor. Phonemic transcription is used in dictionaries to show pronunciation.
►Phonemic chart
A poster or large diagram of the phonemic symbols arranged in a particular order.
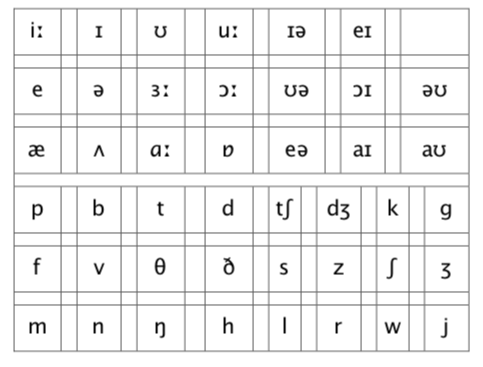

Phonology noun, phonological adjective
The study of sounds in a language or languages.
Schwa
The / W / sound is called the schwa. It is a feature of many weak forms, e.g. / kWn / in I can play tennis.
Silent letter
A letter in a word which is written but which does not influence the pronunciation, e.g. in thumb, the letter b is a silent letter.
Stress:
Contrastive stress
It is used to express an unusual or emphatic meaning in a sentence. It involves stressing the important word according to the different meanings, e.g. It was my AUNT who bought the car (not my uncle) or My aunt bought the CAKE (not the biscuits)!
Primary, main stress
The main stress on a word, e.g. DIFFicult, indiVIDual. The primary stress on a word is marked in the dictionary as follows ‘difficult.
Secondary stress
It is stress on a syllable or word in a sentence that is less strong than the primary (main) stress, e.g. / »kÅntrW«váÄâWl / which has the primary or main stress on / váÄ / and the secondary stress on / kÅn /
Sentence stress
It refers to the way some words in a sentence are stressed. In English these are usually the information-carrying words. In the sentence It was a lovely evening, and the temperature was perfect, the main stress, when spoken, is probably on the word perfect. Stress can therefore be used to show meaning, to emphasise a particular point or feeling.
Word stress
It is the pronunciation of a syllable with more force or emphasis than the surrounding syllables which are said to be unstressed, e.g. umbrella / √m«brelW /.
Strong form
In connected speech many words are not pronounced fully. For example, prepositions, auxiliary verbs, pronouns and conjunctions are usually not pronounced fully and are not stressed. When these words (weak forms) are pronounced fully and are stressed to emphasise a point they become strong forms, e.g. I don’t speak Italian but I can /kæn/ speak a little Spanish in an emergency.
Syllable
A part of a word that usually contains a single vowel sound, e.g. pen = one syllable; teacher = two syllables – teach/er; umbrella = three syllables – um/brell/a.
Voiced sound
To produce a voiced sound, the voice is used, e.g. /b/ in bad, /d/ in dentist. Movement or vibration can be felt in the throat. Vowels in English are voiced.
Vowel
A sound in which the air is not blocked by the tongue, lips, teeth etc. Movement or vibration is felt in the throat because the voice is used. The letters a, e, i, o, u and sometimes y are used to represent these sounds.
See consonant and diphthong.
Weak form
If a word is unstressed, the weak form of vowels may be used, e.g. I can (/ kWn /) speak Italian, French, English and Spanish. The sound / W / is called schwa.